Contents
The rivers play important role in the economic development of any country. In India, rivers play an important role in irrigation, transportation, fishing. Due to this, the rivers in India are tightly bound to Indian tradition and culture. Since ancient times, rivers are worshipped as God/Goddess since they are considered very sacred. India has a rich resource of rivers and in almost every part of India, there is a nearby river.
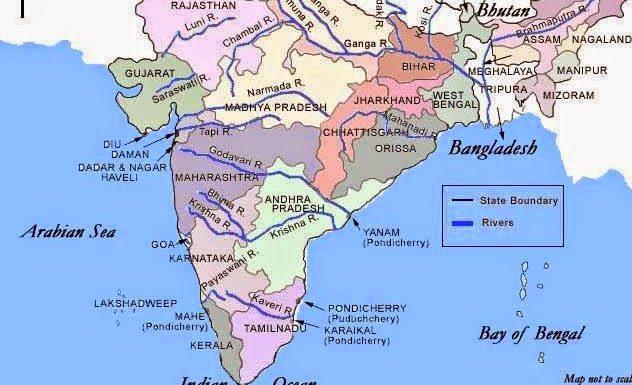
Classification of Rivers of India
- Perennial and Non- Perennial River: If a river is originating from mountains or they get water throughout the year then they are considered as Perennial River. On the other hand, rivers originating from plateau region are called as Non- Perennial Rivers. Non- Perennial Rivers do not have enough waters for the whole year. Perennial rivers of India includes Ganga, Yamuna, Indus, Brahmaputra, Narmada, Mahanadi, Tapti, Ghagra(Saraswati), Sutlej and Thamiraparani(only perennial river from the south).
- (Peninsular Rivers ) East flowing & West Flowing Rivers: The Peninsular Rivers originate in the Western Ghats. They have a large seasonal fluctuation in volume as they are solely fed from rainfall. These rivers flow in valleys with steep gradients. Major rivers of the Peninsula such as Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery flow eastwards on the plateau and drain into the Bay of Bengal. The rivers which end in the Bay of Bengal are called “East flowing” rivers. If the river empties into the Arabian Sea, it is called “West Flowing” rivers. In India, all major rivers are “east-flowing” rivers. The west flowing rivers of India includes Narmada River, Tapti River, Mahi River and Sabarmati River.
- Inland Drainage River: The river which does not empty itself into any sea, and ends with any lake or any other water body is known as Inland Drainage River. The best example of Inland Drainage River in India is Luni River which does not fall into the Arabian Sea but ends up in Rann of Kutch.
- On the basis of their origin.
- The Himalayan mountain range.
- From Satpura and Vindhya range.
- From Western Ghats region.
- The Indus River System
List of Major Rivers in India
| Sl. No. | River | Length (km) | Origin | End |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Indus | 2,900 | Originates in Tibetan plateau, Enters India in J&K | Merges into Arabian sea near Sindh |
| 2. | Brahmaputra | 2,900 | Himalayan Glacier in Tibet, but enters India in Arunachal Pradesh | Merges with Ganga and ends in the Bay of Bengal |
| 3. | Ganga | 2,510 | Gangotri Glacier (Bhagirathi), Uttarakhand | Bay of Bengal |
| 4. | Godavari | 1,450 | Starts in Maharashtra and passes through 7 Indian states | Empties in the Bay of Bengal |
| 5. | Narmada | 1,290 | Starts from Amarkantak, Madhya Pradesh | Drains into Arabian sea via Gulf of Cambay |
| 6. | Krishna | 1,290 | Originates in the Western Ghats near Mahabaleshwar in Maharashtra | Ends in the Bay of Bengal near Andhra Pradesh |
| 7. | Mahanadi | 890 | Originates from Dhamtri, Chhattisgarh | Ends in the Bay of Bengal in Odisha |
| 8. | Kaveri | 760 | Talakaveri in the Western Ghats in Karnataka | Ends in the Bay of Bengal |
State-Wise Rivers
State-Wise details of Rivers Covered
| S. No. | State | River |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | Godavari & Musi |
| 2 | Bihar | Ganga |
| 3 | Delhi | Yamuna |
| 4 | Goa | Mandovi |
| 5 | Gujarat | Sabarmati |
| 6 | Haryana | Yamuna |
| 7 | Jharkhand | Damodar, Ganga & Subarnarekha |
| 8 | Karnataka | Bhadra, Tungabhadra,Cauvery, Tunga & Pennar |
| 9 | Kerala | Pamba |
| 10 | Madhya Pradesh | Betwa, Tapti, Wainganga, Khan, Narmada, Kshipra, Beehar, Chambal & Mandakini. |
| 11 | Mahrashtra | Krishna, Godavari, Tapi and Panchganga |
| 12 | Nagaland | Diphu & Dhansiri |
| 13 | Orissa | Brahmini & Mahanadi |
| 14 | Punjab | Satluj |
| 15 | Rajasthan | Chambal |
| 16 | Sikkim | Rani Chu |
| 17 | Tamil Nadu | Cauvery, Adyar, Cooum, Vennar, Vaigai & Tambarani |
| 18 | Uttar Pradesh | Yamuna, Ganga & Gomti |
| 19 | Uttranchal | Ganga |
| 20 | West Bengal | Ganga, Damodar & Mahananda |
Peninsular Rivers India – Flowing East to West
| Rivers | Length (KM) | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Luni |
| |
| Sabarmati |
| |
| Mahi |
| |
| Narmada |
| |
| Tawa |
| |
| Tapi |
| |
| Periyar |
|
Peninsular Rivers India – Flowing West to East
| Rivers | Length (KM) | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Mahanadi |
| |
| Godavari |
| |
| Penganga |
| |
| Krishna |
| |
| Tungabhadra |
| |
| Bhima |
| |
| Kaveri |
| |
| Penner |
| |
| Vaigai |
|
The Ganga River System
The Ganga River System includes the following rivers (10 major rivers plus Damodar river and Hugli river):
| Rivers | Length (KM) | Origin | End |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ganga | 2,525 | Gangotri Glacier (Bhagirathi), Uttarakhand | Bay of Bengal |
| Yamuna | 1,376 | Yamunotri Glacier, Uttarakhand | Merges with Ganga at Allahabad (Triveni Sangam – Kumbh Mela spot |
| Brahmaputra | 1,800 | Himalayan Glacier in Tibet, but enters India in Arunachal Pradesh | Merges with Ganga and ends in Bay of Bengal |
| Chambal | 960 | Tributary of Yamuna river, starting at Madhya Pradesh | Joins Yamuna river in UP |
| Son | 784 | Tributary of Ganga, starting at Amarkantak, Madhya Pradesh | Joins Ganga just above Patna – also considered part of Vindhya river system |
| Gandak | 630 | Nepal; Ganges tributary at Indo-Nepal border (Triveni Sangam) | Joins Ganga near Patna |
| Kosi | 720 | Starts from Bihar near Indo-Nepal border | Joins Ganga near Katihar district of Bihar |
| Betwa | 590 | Tributary of Yamuna, rises at Vindhya region, MP | Joins Yamuna at Hamirpur in UP |
| Gomti | 900 | Tributary of Ganga, starting at Gomat Taal, UP | Joins Ganga in Varanasi district |
| Ghaghra | 1080 | Himalayan Glacier in tibet, tributary of Ganga | Joins Ganga in Bihar |
| Hugli (Hooghly) | 260 | Tributary of Ganga near West Bengal | Merges with Ganga at the Bay of Bengal |
| Damodar | 592 | Tributary of Hugli near Chandwar, Jharkhand | Merges with Hugli in West Bengal |
Although Hugli and Damodar rivers are not considered the most important rivers of the Ganga river system.
The Indus River System
The Indus River System includes the following 6 major rivers:
| Rivers | Length (KM) | Origin | End |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indus | 3180 | Originates in Tibetan plateau, Enters India in J&K | Merges into Arabian sea near Sindh |
| Chenab | 960 | Upper Himalayas in the Spiti district of Himachal Pradesh | Merges with Indus |
| Jhelum | 725 | Tributary of Chenub river, Punjab | Merges with Chenab at Jhang (Pakistan) |
| Ravi | 720 | Starts from Bara Bhangal, Kangra district, Himachal Pradesh | Joins Chenab in Pakistan |
| Sutlej | 1500 | Tributary of Indus river, originates at Rakshastal, Tibet | Meets Beas river in Pakistan and ends at Arabian sea |
| Beas | 470 | Rises at Himalayas in central Himachal Pradesh | Joins Sutlej river in Punjab, India |
Western Ghats Rivers
Western Ghats Rivers:
| Rivers | Length (KM) | Origin | End |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kaveri | 765 | Talakaveri in the Western Ghats in Karnataka | Ends in the Bay of Bengal |
| Krishna | 1400 | Originates in the Western Ghats near Mahabaleshwar in Maharashtra | Ends in the Bay of Bengal near Andhra Pradesh |
| Godavari | 1465 | Starts in Maharashtra and passes through 7 Indian states | Empties in the Bay of Bengal |
| Tungabhadra | 531 | Tributary of Krishna river staring at Karnataka | Joins Krishna river along the border of Telangana and Andhra Prades |
Vindhya and Satpura Ranges rivers
Vindhya and Satpura Ranges rivers:
| Rivers | Length (KM) | Origin | End |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tapti | 724 | Rises in Eastern Satpura Ranges, Madhya Pradesh | Empties into Gulf of Khambat, Gujarat |
| Mahi | 580 | Rises in Madhya Pradesh | Flows into Arabian sea from Gujarat |
| Narmada | 1315 | Starts from Amarkantak, Madhya Pradesh |
Other Important Notes on Indian rivers to remember:
- River Saraswati was considered to be a mythical river and is part of the Hindu Triveni Sangam mythology of the confluence of Ganga, Yamuna and Saraswati rivers. Recent studies have shown that the Saraswati river was flowing under the ground and meeting Ganga and Yamuna at the Kumbh Mela spot.
- Meghna a major river in Bangladesh is a tributary if Indian Brahmaputra river and also empties into the Bay of Bengal.

Please give tributaries of rivers