Contents
The geographical name of Gujarat is supposed to be derived from Gurjara. The literary meaning of Pratihara is ‘door keeper.’
The Gurjara Pratihara dynasty kings were followers of Hinduism. It is believed that their ancestor Lakshmana served as a doorkeeper to his brother Rama.
They ruled between mid-8th and 11th century A.D. over northern and western India.
The Pratiharas stood as a fortification of India’s defence against the hostility of the Muslims from the days of Junaid of Sind (725. A.D.) to Mahmud of Ghazni.
Capital of Gurjara Pratihara dynasty was first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj.
Colonel James Todd wrote “Annals of Rajputana” or “ Rajasthan Kathavali”, According to James Todd Rajputs were descendants of HUNs. Somadeva Suri’s “Kathasaritha Sagara” also gives details of Rajputs. Rashtrakuta poet Pampa also mentions Gujara in his book.
Rulers:
Bhoja
The Gwalior inscription mentioned the early history of the family founded by King Bhoja in the 7th century.
Nagabhatta I (725-740)
Nagabhatta is the real founder of the Gurjara Pratihara dynasty. He established the capital at Avanti in Malwa.
He came into conflict with Rashtrakuta king Dhruva (tripartite warfare for Kannauj)
Junaid, another Arab commander defeated by him in Battle of Rajasthan.
Vatsaraja (780–800)
Nagabhtta was followed by Vatsaraja.
Vatsaraja captured Kannauj and came in direct conflict with the Palas of Bengal. He defeated Dharmapala.
In 786 AD the Rastrakuta King Dhruva defeated him.
Nagabhatta II (805-33)
Nagabhatta was initially defeated by Rastrakuta King Govinda III but later recovered and captured Kannauj.
He is best known for rebuilding the Somnath Temple in 815. Somnath Temple was destroyed by the Arab armies of Junayad in 725 AD.
This was a large structure of Red Sandstone which was again destroyed in 1024 by Mahamud of Ghazni.
Mihirabhoja (836-85)
Mihirabhoja ruled long for 46 years. He defeated Rashtrakuta king Krishna-II and captured the region of Malwa and Gujarat.
Mihirabhoja was a devotee of Vishnu, and adopted the title of ‘Adivaraha.’
Mihirbhoj was mentioned by Arab travellers. Abu Suleman called him king Juzr, al-masudi called king Baura.
Mahendrapala (885-908)
Son of Mihirabhoja, was also known as ‘Mahendrayudha’, and ‘Nirbhayanarendra.’
Rajashehara, Sanskrit poet was in his court.
Mahipala
Arab scholar, Al-Masudi, visited his court in 915-916.
Rajyapala
The last king Rajyapala was defeated by Krishna 3 of Rashtrakuta and Ghazni Mohammed.
Decline of the Pratihara Dynasty
The Rashtrakuta king, Indra-II again attacked Kanauj between A.D. 915 and A.D. 918 and destroyed it.
Krishna III was another Rashtrakuta ruler who invaded north India in about A.D. 963.
He defeated the Pratihara rulers. This led to the decline of the Gurjara Pratihara Empire.
Rajyapala was the last Gurjara Pratihara king. In his time empire was reduced to Kanauj and nearby areas.
The Pratihara power came to an end after Mahmud of Ghazni attacked the kingdom in 1018 A.D.
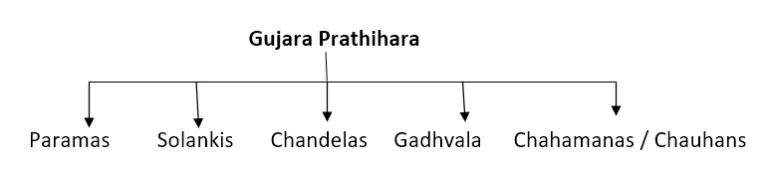
This led to fragmentation of Rajput
Architecture
There are notable examples of architecture from the Gurjara-Pratihara era, including sculptures and carved panels. They started Maru- Gujara style of architecture.
Bateshwar Hindu temples complex: Located near Gwalior(MP) Dedicated to Shiva, Vishnu and Shakti.
Baroli temple complex


